Report
- Complex Global Simulation
- Report
A paper on an international joint research project in which Prof. Y. Todo participates has been published in Nature Physics
An international collaboration involving Dr. J. Dominguez-Palacios and Dr. M. Garcia-Munoz of the University of Seville, Spain, and Prof. Y. Todo of the Complex Global Simulation Unit of the National Institute for Fusion Science has been published in Nature Physics on January 6, 2025.
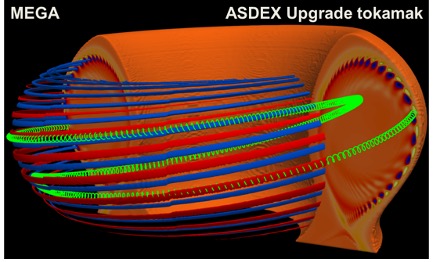
Dr. Dominguez-Palacios used MEGA, a hybrid simulation code developed by Professor Todo, to investigate the effects of energetic particles on the edge localized mode (ELM), a heat and particle ejection phenomenon in fusion plasmas.
As a result, the simulation reproduced an abrupt and large crash that characterizes ELMs, and revealed that energetic particles have a significant effect on the amplitude and frequency spectrum of ELMs.
This study advances the understanding of the physics underlying ELM crashes in the presence of energetic particles and highlights the importance of energetic particles in the optimization of ELM control techniques.
【Publication】
【Nature Physics press release】
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-024-02737-0
【The University of Seville press release】
(English) https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/1069991
